Pharmacists can now assess for minor ailments and prescribe you medication. All you need is your health card.
You can also click on the button below to learn more about the minor ailment system as described by the Ontario Pharmacist Association.
Call us today if you have any questions or to check availability for assessment!
Click on the various tabs to learn more about each of the available minor ailments.
- Painful Menstrual Periods
- Musculoskeletal Sprains and Strains
- Pink Eye
- Oral Candidiasis (Thrush)
- Impetigo
- Allergic Rhinitis
- Cold Sores
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Hemorrhoids
- Insect Bites and Stings
- Dermatitis
- Tick bites, post-exposure prophylaxis to prevent Lyme disease
- Urinary tract infections (uncomplicated)
What you need to know!
Some women experience painful menstrual periods, also known as dysmenorrhea, which can include abdominal cramps, back pain, headaches, fatigue, and nausea. While this is a common condition and usually not serious, it can be caused by an infection or ovarian cysts, or be related to endometriosis. To manage painful periods, women can use heating pads or take over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or naproxen. Regular exercise may also help prevent symptoms. If the pain persists, women should consult their healthcare provider to be examined for possible causes and to explore other treatment options such as birth control pills.
If you have a sports injury, remember RICE: Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation for the first two days or until the swelling goes away. Rest the injured area, apply ice every few hours, bandage the injury, and raise the injured area above the level of the heart. Seek medical attention if you think you need medication for pain and swelling or if the injury does not improve within two weeks or the pain worsens despite treatment.
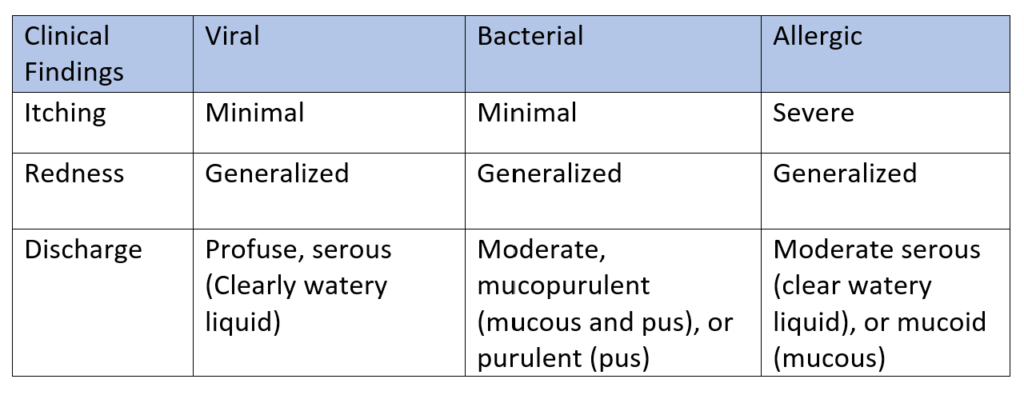
Different cases of pink eye show different symptoms check the table and see what relate to you.
Oral candidiasis, also known as thrush, is an infection in the mouth or throat caused by Candida, a yeast-like fungus. It appears as whitish or yellowish patches on the tongue or inside the cheeks. Anyone can get thrush, but it is more common in newborn babies, people who wear dentures, have dry mouth, certain diseases or take certain medications. To prevent thrush, practice good oral hygiene, see a healthcare provider if you have dry mouth, avoid mouthwashes with a lot of alcohol, disinfect dental appliances and dentures, and rinse your mouth with water after using inhaled corticosteroids. If you have thrush, see a healthcare provider for medication, swish and swallow the recommended dose, and throw away your old toothbrush.
Dermatitis is a condition that causes inflammation of the skin. It is characterized by redness, itching, and swelling of the affected area. There are different types of dermatitis, including atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis, and stasis dermatitis. The causes of dermatitis can be varied, ranging from genetic predisposition to exposure to irritants or allergens. Treatment options include topical creams and ointments, oral medications, and lifestyle changes such as avoiding triggers or using gentle skin care products.
Tick bites occur when a tick, a small parasitic insect, attaches itself to a human or animal host and feeds on their blood. Ticks can carry various diseases, including Lyme disease, which is caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi.
Post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) refers to the use of antibiotics to prevent the development of Lyme disease after a tick bite. PEP is recommended in cases where the tick has been attached for more than 36 hours and where there is a high risk of Lyme disease transmission.
The choice of antibiotics and duration of treatment for PEP may vary depending on the patient’s age, medical history, and the type of tick that caused the bite. It is important to remove the tick as soon as possible and to clean the bite area thoroughly with soap and water. Early detection and treatment of Lyme disease can help prevent the development of more serious complications, such as joint pain, neurological problems, and heart issues.
Uncomplicated urinary tract infections (UTIs) are bacterial infections that occur in the urinary tract, including the bladder, urethra, and occasionally the kidneys. These infections are more common in women than men and can cause symptoms such as frequent urination, burning or pain during urination, and lower abdominal pain.
The treatment for uncomplicated UTIs typically involves a short course of antibiotics to eliminate the bacteria causing the infection. Pain relief medication may also be prescribed to alleviate discomfort. Drinking plenty of fluids and urinating frequently can help flush out bacteria from the urinary tract. It is important to complete the full course of antibiotics even if symptoms improve, to prevent the infection from returning or worsening.








